Subtotal: $0.00
AC/DC Motor Theory
Overview
The AC/DC Motor Theory course was specifically developed for electricians and electronic technicians as well as for the multi-craft training needs of process and manufacturing facilities. This course consists of 11 interactive, on-line lessons that address AC and DC motor theory.
Objective
- Identify the components of an AC Motor and explain their function.
- Explain the basic principles of magnetism.
- Interpret the characteristics of a current as represented on a sine wave.
- Describe the effect of AC current on a conductor.
- Describe the methods of increasing magnetic flux in a conductor.
- Explain how a rotating field is created in an AC Motor.
- Explain and be able to calculate synchronous speed.
- Explain induction and its effect on a rotor.
- Explain the relationship between phased current and rotor spin.
- Explain slip and know its formula.
- Describe the design of a squirrel cage rotor and function of components.
- Describe the design of a wound rotor and function of a wound rotor’s components.
- Define torque and explain its role in motor operation.
- Explain the design of a reluctance motor and how it works.
- Explain the design of an externally excited motor.
- Explain how an externally excited motor works.
- Explain the function of a motor starter and the most common types of motor starters.
- Describe a variable speed drive and its effect on voltage and frequency.
- Distinguish a single-phase motor from a three-phase motor.
- Explain the design of a split-phase motor and how it works.
- Explain the design of a capacitance start motor and how it works.
- Identify the general characteristics and advantages of a DC motor.
- Identify the basic components of a DC motor.
- Explain the function of DC motor components.
- Identify the components of the armature and brush assembly; explain their function.
- Explain the effect of armature current on the main flux field and motor action
- Explain the process of commutation and how it maintains direct current in a DC motor.
- Describe how the number of windings and commutator segments effects torque and mechanical power of a DC motor.
- Explain how armature reaction shifts the neutral plane in a DC motor.
- Explain how armature reaction affects motor operation.
- Explain what measures will correct armature reaction.
- List the requirements for induced voltage in a motor.
- Explain counter-EMF.
- Explain the design of a series wound DC motor and how it works.
- Explain the design of a shunt wound DC motor and how it works.
- Explain the design of a compound wound DC motor and how it works.
- Explain the design of a permanent magnet DC motor and how it works.
- Explain how a universal motor runs off of DC power.
- Explain the design of a brushless DC motor and how it works.
- Explain why a reduced voltage starter is sometimes needed in a motor.
- Explain how a reduced voltage starter works.
- Explain what determines the direction of rotation of a DC motor.
- Explain how a reverse contactor works.
- Explain how to control the speed of a DC motor.
- Explain how a tapped resistor works.
- Explain a DC drive’s control system and how it works
Modules
Showing all 11 results
-

Three-Phase Motors – Part 1
-

Introduction to AC Components and Motors
-
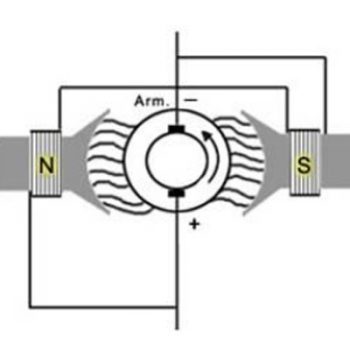
DC Motor Controls
-
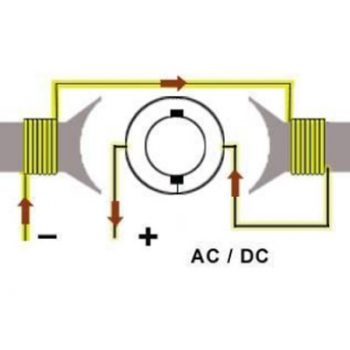
Permanent Magnet, Universal, and Brushless DC Motors
-
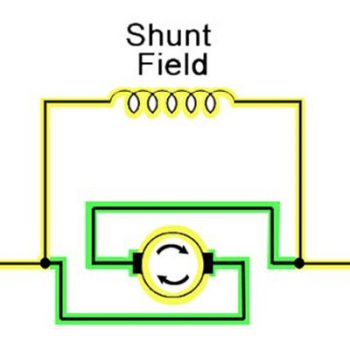
Series, Shunt, and Compound DC Motors
-
Armature Reaction, Compensation, and Induced Voltage
-
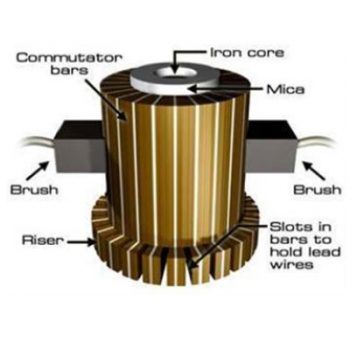
Introduction to DC Motor Theory
-
Introduction to DC Motors
-

Single-Phase Motors
-

Three-Phase Motors – Part 2
-

Advanced AC Motor Principles


